ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND INDICATORS IN GEORGIA
HOTEL PRICE INDEX
PMC RESEARCH - IFO GEORGIAN ECONOMIC CLIMATE
BLACK SEA BULLETIN
QUARTERLY TOURISM UPDATE
ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND INDICATORS IN UKRAINE
SECTOR SNAPSHOTS
EMPLOYMENT TRACKER
MACRO OVERVIEW
BAG Index
Profile Of Bilateral Relations

Issue 131: Foreign Direct Investment Trends in Georgia
01-Nov-2021
For developing countries, attracting FDI has great potential to serve as a tool to achieve higher economic growth through reducing unemployment, increasing exports, boosting productivity, and improving capital inflows. During the last two decades, Georgia has adopted many reforms to eliminate obstacles in the way of doing business and to attract foreign investors. As a result, Georgia became one of the best performers in the world according to international indices on doing business and openness to investments, and recorded substantial growth in FDI, especially in the period of 2014-2017. However, those reforms have not been sufficient to ensure a prolonged steady inflow of FDI nor have they maximized the potential gains from foreign investment.
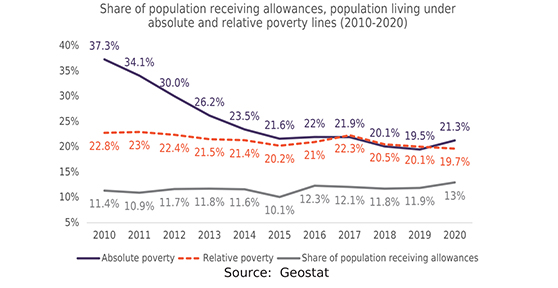
Issue 130: Poverty in Georgia (2010-2020)
12-Oct-2021
Poverty alleviation remains one of the biggest challenges for the world, including Georgia. Methods applied to determine the poverty rate vary from country to country, so in order to gain a broad understanding of the current situation regarding poverty in Georgia at the international level, it is important to take into account a variety of indicators. In 2020, GDP per capita in Georgia amounted to 4279 USD, ranking it 122nd in the world and 3rd among Eastern Partnership (EaP) countries. Meanwhile, the Human Capital Index (HCI) calculates the contributions of health and education to worker productivity with Georgia scoring 0.57 in 2020, ranking 85th out of 174 countries world and having the lowest score among EaP countries.Multidimensional poverty encompasses various forms of deprivation experienced by poor people such as poor health, lack of education, inadequate living standards, poor quality of work and the threat of violence. In 2019, 3.8% of the population in Georgia was multidimensionally poor, ranking 57th out of 120 countries in the world and first among EaP countries. The Gini Index measures income distribution within a society. In 2021, Georgia scored 36.4 on the Gini Index, ranking 76th out of 165 countries and having the highest inequality rate among EaP countries. In terms of life expectancy, in 2020 average life expectancy in Georgia was 74.2 years, ranking it 101st in the world and 3rd among EaP countries. Taking into account these indicators, Georgia, on an international level, is an upper-middle-income country with moderate rates of inequality and life expectancy. Due to its poor educational and healthcare systems, Georgia has been unable to mobilize its human capital to achieve a higher level of economic development.
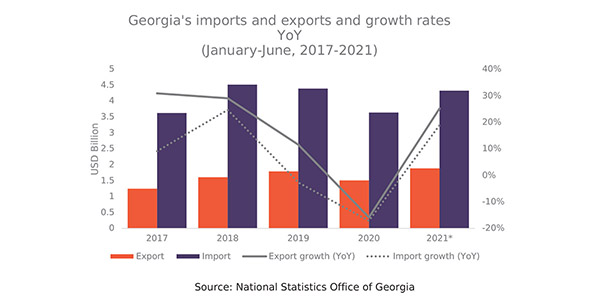
Issue 129: Georgia’s External Trade (January-June, 2017-2021)
01-Sep-2021
In the first half of 2021, external trade turnover in Georgia amounted to 6.2 bln USD, which is 20.7% more than corresponding period of 2020 and 0.5% more than the prepandemic period of January-June 2019.
Georgian exports amounted to 1.9 bln in January-June 2021, which is 25.2% more than in January-June of 2020 and 5.3% more than in January-June of 2019. Moreover, Georgian imports recorded 4.3 bln USD, which is 18.9% more than in the first half of 2020 and 1.5% less than in the corresponding period of 2019.
In the first half of 2021 Georgian trade deficit increased by 0.3 bln USD (14.5%), compared to the first half of 2020, and decreased by 0.16 bln USD (6.1%), compared to the corresponding period of 2019 and amounted to 2.44 bln USD.
In the period of January-June 2021, compared to January-June of 2020, trade turnover increased with the EU (9.9%), Russia (24.8%) and China (22.7%). However, compared to the corresponding period of 2019, trade turnover increased with Russia (12.3%) and China (27.9%), but decreased with the EU (-14%).
Georgia’s main total trade partners in the first half of 2021 were Turkey (15.2%), Russia (11.8%) and China (10.5%). Main export partners were China (15.4%), Russia (14%) and Azerbaijan (8.4%). Moreover, main import partners were Turkey (18%), Russia (10.8%) and China (8.4%).
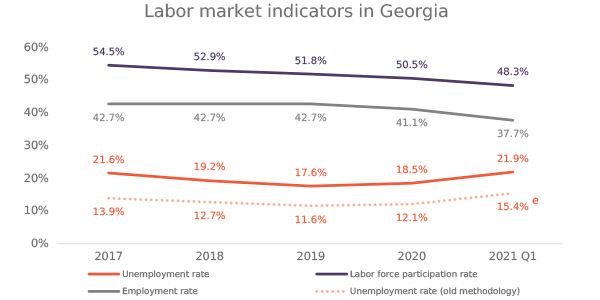
Issue 128: Unemployment in Georgia (2017-2020)
27-Jul-2021
In 2021, unemployment remains an unresolved obstacle for the Georgian economy and society’s most pressing problem. Over the years, diverse public opinion polls have indicated that unemployment is the most important issue at national level. For instance, in 2020, according to a public attitudes poll conducted by the National Democratic Institute, for 46% of respondents, the main challenge they were facing was unemployment.This issue focuses on changes in unemployment trends in Georgia in the period of 2017-2020 and provides an analysis of the effects of the COVID-19 crisis on unemployment in the country.

Issue 127: Remittance Inflows in Georgia during Covid-19 Crisis
22-Jun-2021
This bulletin focuses on remittance inflows into Georgia in 2020 and its development in 2021.
The social and economic stability of Georgia strongly relies on the money sent from emigrants to their families. Based on World Bank Data, in 2019, in terms of dependence on remittance inflows, Georgia ranked 21st in the world, with remittance inflows to GDP ratio. Moreover, the study conducted by the State Commission on Migration Issues revealed that in 2016 money sent by every second emigrant to their families accumulated half or 3/4 of family budget, and for the 15% of families remittance was the only source of income in Georgia.
The COVID-19 pandemic and imposed restrictions hindered economic activity in nearly every country, resulting in a negative effect on wages and employment for migrant workers and consequently, drying up of remittance inflows. In 2020 due to the emerged crises and uncertain situation, the World Bank projected shrinking remittance flows for low and middle-income countries by 7.2%3, while the IMF forecasted a 15%4 decline for Georgia. However, despite the crisis and pessimistic predictions in Georgia, the volume of remittance inflows in 2020 compared to 2019 has increased by 8.8% and reached the highest figure in the past decade - 1.9 BLN USD, amounting to 11.9%, expressed as a percentage to GDP.
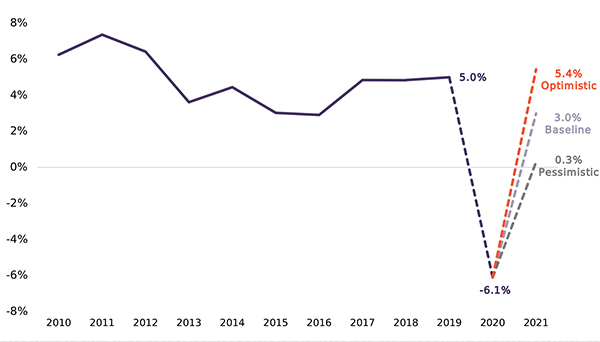
Issue 126: GDP and Employment in Georgia: Forecasts for 2021
04-Mar-2021
In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic heavily disrupted the world, causing both a global health emergency and a global economic crisis. While almost every country and every sector have been affected, economies reliant on the service sector, and especially the tourism industry, such as Georgia, have suffered notably. Indeed, measures taken to contain the spread of the virus have had an especially negative impact on the economy. Preliminary estimates suggest a decline in Georgia’s real GDP in 2020 of 6.1%, the sharpest drop since 1994.In this issue, we provide forecasts for the performance of the Georgian economy for 2021, namely regarding its real GDP growth rate, sector-specific growth rates, and employment.
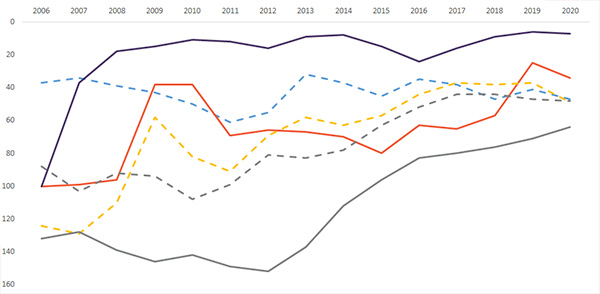
Issue 125: Georgia in International Rankings
25-Jan-2021
International rankings and indicators help us to understand and assess how countries are performing in different areas. In this bulletin, Georgia’s positions in international rankings and their dynamics are reviewed based on recent data, and these are also compared to other Eastern Partnership (EaP) countries (Armenia, Azerbaijan, Moldova, Ukraine, and Belarus).
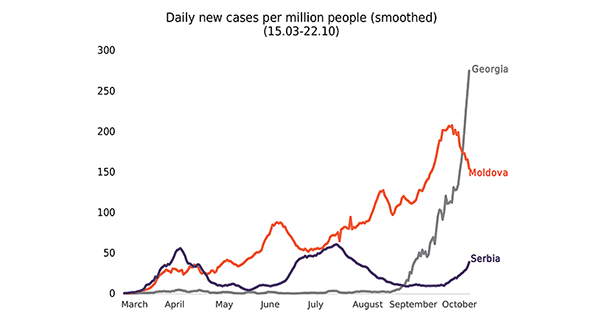
Issue 124: Overview of COVID-19 in Eastern Europe and Central Asia Including Case Studies of Georgia, Moldova and Serbia
22-Oct-2020
The COVID-19 pandemic, and the ensuing economic shock, has prompted governments all around the globe to act swiftly and decisively to mitigate the health and economic impacts of the crisis. Each country has responded in its own way, and it is useful to look at these different responses to identify good practices. In this issue, we look broadly at countries in Eastern Europe and Central Asia, and present three case studies of Georgia, Moldova, and Serbia respectively, including an analysis of the fiscal measures these countries have taken and an overview of the impacts of the pandemic.

Issue 123: Employment and Income Dynamics in Georgia
05-Oct-2020
In August 2020, the number of employees receiving salaries recovered almost fully and stood at only 1% less than the corresponding month of last year;
During the period of January-August 2020, the month of May saw the largest drop in the number of employees receiving salaries (a dip of 9% or 74 951), compared to the corresponding period of 2019;
The month of April experienced the biggest decline in the number of employees for four out of the five higher-income categories, with the highest decline (23%) recorded in the number of people earning more than GEL 4800 per month;
The total average monthly earnings of employees in Q2 of 2020 amounted to GEL 1150.1, which represents a 3% decrease compared to Q2 of 2019;
According to the data obtained from HR.ge and Jobs.ge, the drop in demand for labor started in March and reached its peak in April, when HR.ge and Jobs.ge experienced an 87% and 78% year over year (YoY) decline in new vacancies posted, respectively. The YoY growth rates started recovering towards the baseline in May, but then registered a significant decline in August.
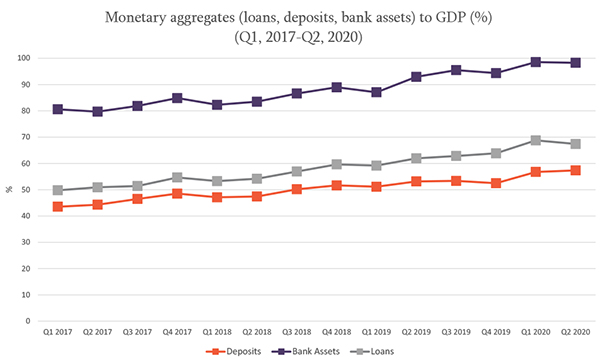
Issue 122: Banking Sector in Georgia (2017-2020)
17-Sep-2020
By the end of the second quarter of 2020, loans and deposits, expressed as a percentage of GDP, increased by 3.6 and 4.9 percentage points, respectively, compared to the beginning of the year;
By the end of the second quarter of 2020, bank assets, expressed as a percentage of GDP, increased to 98.4%;
By the end of July of 2020, the volume of loans was increased by 19%, compared to July of 2019;
The average interest rates on loans in January-July of 2020 denominated in national currencies were 0.9 percentage points higher than in January-July of 2019, while the average interest rates on loans denominated in foreign currencies were 0.8 percentage points less;
By the end of July of 2020, the volume of deposits in Georgia was increased by 21%, compared to July of 2019;
The average interest rates on deposits in January-July of 2020 denominated in national currencies were 1.2 percentage points higher than in January-July of 2019, while the average interest rates on deposits denominated in foreign currencies were 0.4 percentage points less;
In January-July of 2020 trade had the highest share of total loans with 29.5%;
In January-July of 2020, share of construction in total loans increased by 3.6 percentage points, while share of financial intermediation decreased by 8.2 percentage points, compared to the corresponding period of 2019;
According to the World Bank, Georgia’s ratio of non-performing loans to total loans decreased in 2019, compared to 2018, by 0.8 percentage points and dropped to 1.9%;
By the end of July of 2020 the rates of dollarization on loans and deposits were increased by 0.3 and 8 percentage points, compared to the corresponding period of 2019. The rates rose to 56.9% and 61.3%, respectively.
- Periodic Issues
- ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND INDICATORS IN GEORGIA
- HOTEL PRICE INDEX
- PMC RESEARCH - IFO GEORGIAN ECONOMIC CLIMATE
- BLACK SEA BULLETIN
- QUARTERLY TOURISM UPDATE
- ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND INDICATORS IN UKRAINE
- SECTOR SNAPSHOTS
- EMPLOYMENT TRACKER
- MACRO OVERVIEW
- BAG Index
- Profile Of Bilateral Relations